Ethereum vs Ethereum Classic: Understanding the Key Differences

This blog post will cover:
- At‑a‑Glance: Difference between Ethereum ETH vs. ETC
- How We Got Here: The DAO Hack & the Fork
- How They Work Today
- Scalability & Fees in Practice
- Security Track Records & Risks
- Ecosystem & Developer Activity
- Which One Fits Your Goal? (Decision Guide)
- How to Swap on SimpleSwap
- FAQs & Common Misconceptions
Ethereum and Ethereum Classic might share a name, but their paths have been drifting apart for years. What started as a shared version of the Ethereum eventually split after a controversial decision that shook the early crypto community.
Since then, both networks have stuck to their own philosophies - one pushing for rapid evolution, the other holding tight to the idea that code shouldn’t be rewritten. If you’re trying to figure out which one fits your goals, it helps to understand how that split happened - and what’s happened since.
At‑a‑Glance: Difference between Ethereum ETH vs. ETC
If you're new to blockchain technology, one thing that'll probably trip you up early is figuring out the actual difference between Ethereum and Ethereum Classic. On the surface, they look similar - and that’s because they used to be the same thing. But in 2016, a major DAO hack split the community. One side wanted to reverse the hack and recover the stolen funds by rewriting part of the original Ethereum blockchain. The other side saw that as crossing a line - you don’t change the ledger, period. That disagreement led to a hard fork, and suddenly there were two separate blockchains.
Since then, the second-largest cryptocurrency has evolved fast. It’s now on Proof of Stake, meaning no more traditional mining, and it uses way less energy - almost 100% less. It's also scaling aggressively with things like Layer 2 solutions (like Optimism), which help bring down costs and speed things up. When comparing ETH vs ETH Classic, the classic network went in the opposite direction - no major changes, no fork reversals, just a strong belief in keeping the chain exactly as it was. It still runs on Proof of Work, has super low fees, but has faced a few security issues like 51% attacks. The ethereum classic users are smaller in number, and progress moves slower by design.
Right now, Ether trades at about $3,855.80 (down 0.63%), and Ethereum Classic sits around $22.17 (down 4.65%).
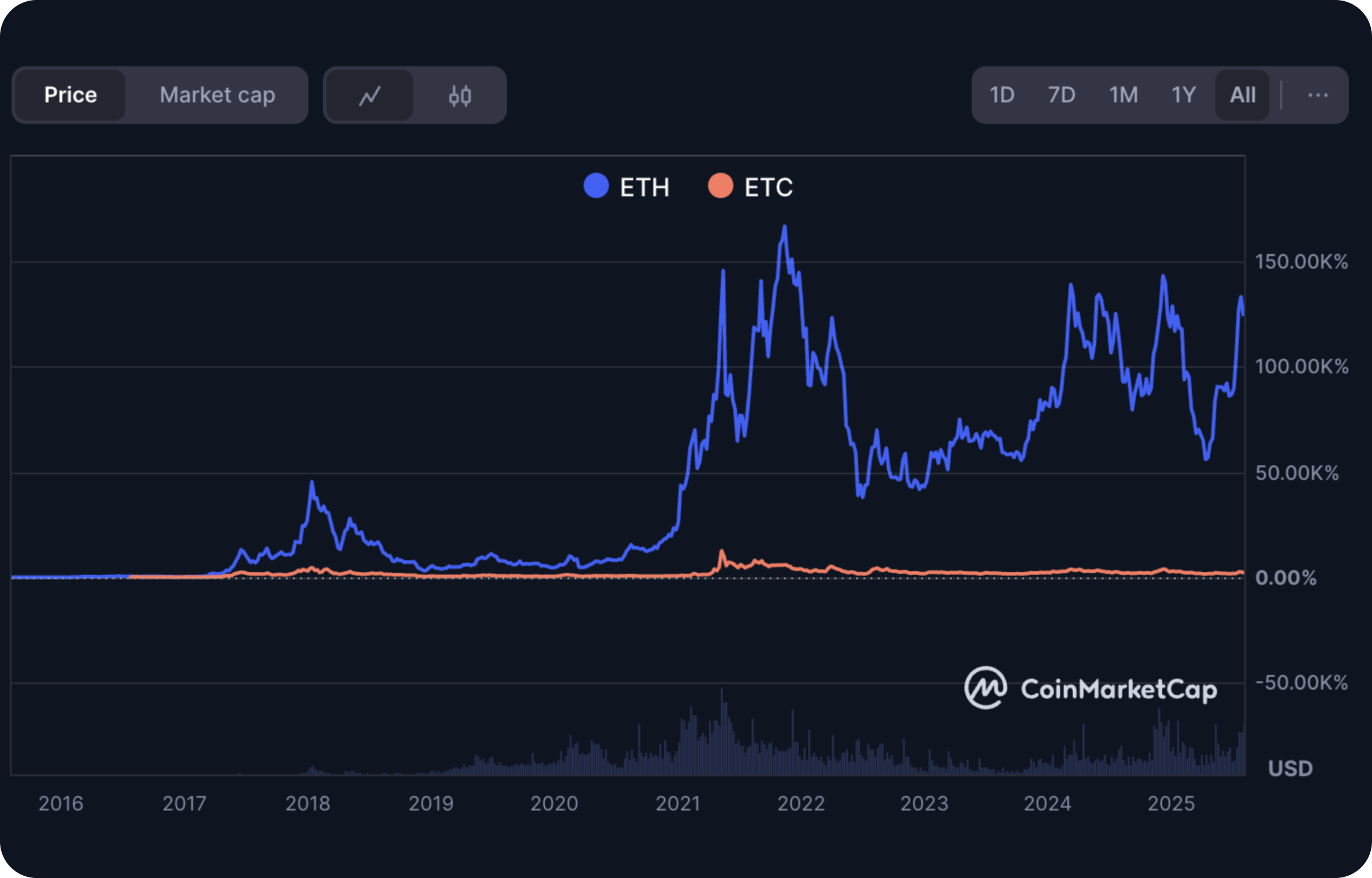
Source: CoinMarketCap
Prices and fees bounce around, so take that as a snapshot - not a prediction.
Feature | Ethereum (ETH) | Ethereum Classic (ETC) |
Consensus | Proof-of-Stake (PoS) | Proof-of-Work (ETCHash) |
Token economics | No fixed cap; burn via EIP‑1559 | Fixed cap (~210.7M; ECIP‑1017) |
Scalability path | L2 rollups; boosted by EIP‑4844 | Limited on-chain scaling |
Security history | Strong post-Merge security | Multiple 51% attacks (2019–2020) |
Ecosystem size | Broad dApp, DeFi, and NFT adoption | Smaller, more niche community |
Typical fees today | L2s often <$0.10; Mainnet ~$3–10 | ~$0.01–$0.05 |
Note: Fees and market metrics fluctuate regularly.
How We Got Here: The DAO Hack & the Fork
Back in 2016, Vitalik Buterin and the Ethereum Foundation were leading a network full of energy and experimentation. The DAO, a big early decentralized autonomous organization, got hacked because of a bug in its code. Millions of dollars’ worth of cryptocurrency vanished overnight. But the real divide came after - people couldn’t agree on what to do.
Some wanted to roll back the blockchain to fix the issue. Others said that went against everything a blockchain stands for. The result was a split: one group moved ahead with changes, and Ethereum Classic remained the original version of Ethereum.
The DAO incident (2016): What happened?
Back in 2016, Ethereum was still pretty fresh. People were excited, trying new stuff, and one of the big ideas at the time was the DAO. It was basically this decentralized investment fund, where anyone could throw in some Ether coins and vote on where the money should go.
It blew up fast - raised something like $150 million, which was insane back then. But then it all unraveled. There was a bug in the code, and someone figured out how to drain the funds. About $50 million vanished. It wasn’t a traditional hack - they didn’t break in, they just took advantage of a flaw no one had noticed. And that’s when everything changed.
This threw the Ethereum community into a full-blown crisis. What should be done? Stick with the principle that blockchains are immutable, no matter the consequences? Or make an exception and rewrite the chain to undo the damage? After a lot of debate, most of the community chose to go with a hard fork, which basically reset the chain to a point before the attack happened and returned the stolen ETH. But not everyone was on board. A smaller group felt that doing so went against everything blockchain was supposed to stand for. They stuck with the original, untouched version of the chain, which later became Ethereum Classic.
“Social consensus” vs. “Code is law”
The real split wasn’t just about fixing a bug - it was ideological. One side believed people should step in when things go wrong. The other believed the consensus mechanism and the code should stand no matter what.
So, Ethereum and Ethereum Classic represent two distinct visions: one based on flexibility, the other on strict immutability. Despite misconceptions, Classic isn’t the fork - it's the untouched chain. That philosophical divide still defines how both are governed today.
How They Work Today
These separate blockchains differ in how they run, from consensus to token rules and governance. These differences between Ethereum Classic vs Ethereum shape how people use them, invest in them, and view their long-term potential across the blockchain network.
Consensus & energy
Since the Merge in 2022, known as Ethereum 2.0, the network uses Proof of Stake. That means no more power-hungry rigs - just people staking their ETH to help keep the network running. The switch reportedly cut Ethereum’s energy use by nearly 100%, which is a big deal for anyone keeping an eye on sustainability.
Ethereum Classic didn’t follow. It stuck with Proof of Work, keeping things as they were. Miners still play the same role they always have, putting in computing power to secure the chain. ETC never changed course - it’s stayed loyal to the original setup. For some, that commitment to the old-school model is a plus. For others, especially those concerned about energy, it’s a reason to lean toward ETH.
Token economics
The economic structures underpinning both Ethereum platforms significantly differ, impacting their long-term investment potential. Ethereum has no fixed token cap; instead, it manages issuance through base-fee burning, implemented via Ethereum Improvement Proposal 1559 (EIP-1559). With each transaction, a portion of the coin is permanently removed (burned), offsetting issuance and often reducing net supply growth. This mechanism introduces a deflationary aspect to Ethereum's tokenomics.
Ethereum Classic, on the other hand, follows a strictly capped-supply model outlined in Ethereum Classic Improvement Proposal 1017 (ECIP-1017). Ethereum Classic, on the other hand, has a fixed cap of around 210.7 million coins, giving its blockchain a more predictable long-term monetary policy.For some investors, that scarcity mirrors Bitcoin approach and makes Classic attractive as a long-term cryptocurrency bet.
Upgrade cadence & governance: ETH roadmap (post-Dencun) and ETC ECIPs.
Ethereum and Ethereum Classic take very different approaches when it comes to how their tokens work. The former doesn’t have a hard supply limit. Instead, it introduced a fee-burning system through EIP-1559, which removes a portion of Ethereum from circulation every time someone makes an operation.
EIP-1559 (Ethereum Improvement Proposal 1559) is a major upgrade to Ethereum’s transaction fee system, introduced in August 2021 as part of the London Hard Fork. It replaced the traditional auction-based gas model with a more predictable system that includes:
A base fee, which is automatically adjusted based on network demand and is burned (permanently removed from circulation), reducing ETH supply.
An optional tip (priority fee), which users can add to incentivize faster processing by validators.
EIP-1559 is designed to improve fee transparency, reduce volatility, and introduce a deflationary pressure on ETH by burning part of every transaction fee.
That burn helps balance out new assets being issued, and in some cases, it even leads to the total supply shrinking over time. It’s not exactly deflationary by default, but it leans that way depending on network activity. Ethereum Classic goes in the opposite direction - its supply is capped.
ECIP-1017 locked Classic’s maximum supply at just over 210 million coins. That fixed limit appeals to people who like the idea of scarcity and predictable issuance, more like Bitcoin. Now, ECIP-1017 (Ethereum Classic Improvement Proposal 1017) is a protocol change implemented on Ethereum Classic that introduced a monetary policy with a fixed supply cap and a deflationary emission schedule.
It set a maximum total supply of approximately 210.7 million ETC.
Introduced a “5M20” schedule, reducing block rewards by 20% every 5 million blocks (roughly every 2.4 years).
This makes ETC’s issuance similar to Bitcoin’s halving model, but with smaller and more frequent reductions.
In short, ECIP-1017 ensures Ethereum Classic has a predictable, capped supply, appealing to users who value scarcity and fixed issuance over flexible monetary policy.
Scalability & Fees in Practice
Scalability and transaction costs are often decisive factors for both users and developers. In the difference between ETH and ETC debate, these differences have become more pronounced since Ethereum’s Dencun upgrade. For many users, especially those transacting frequently, cost predictability and performance impact usability - and both blockchains address those challenges differently.
Ethereum after Dencun (EIP‑4844): L2 fees dropped dramatically; real user impact.
The Dencun upgrade, which went live in March 2024, introduced EIP-4844 (proto-danksharding), a major milestone in Ethereum’s long-term scalability roadmap. This innovation allowed Layer 2 (L2) rollups - like Arbitrum, Optimism, and Base - to store more data cheaply via “blobs,” reducing operation fees by an order of magnitude.
Since Dencun, users have seen substantial drops in L2 costs, often bringing them well below a dollar per transaction. While Ethereum mainnet (L1) fees still spike during periods of congestion - sometimes hitting $10 or more - L2s offer a smoother, cheaper user experience for most daily activities. This development has flipped the old “Ethereum is too expensive” narrative, making the asset more accessible for NFTs, DeFi, and remittances.
ETC fees & throughput
Ethereum Classic, by contrast, operates solely on Layer 1 using Proof of Work and the ETCHash algorithm. ETC has long been known for its low fees - often a fraction of a cent - and relatively consistent throughput.
However, it's important to note that coin’s fee structure reflects lower demand and simpler smart contract usage, not necessarily superior scalability. While attractive for basic transfers or GPU miners, Ethereum Classic lacks the rollup-based scaling strategy that allows Ethereum to process significantly higher volumes without congesting the base layer.
These differences play a big role in how users experience both Ethereum networks and the range of applications they can support.
Security Track Records & Risks
While both Ethereum and Ethereum Classic aim to offer secure networks, their histories and risk profiles tell different stories. The type of security each chain relies on - and the threats they’ve faced - are important for users and developers to understand.
Ethereum Classic’s 51% attack history & MESS mitigation
Ethereum Classic’s use of Proof of Work has opened it up to some serious security issues over the years - especially 51% attacks. That’s when someone controls most of the network’s hash power and can basically mess with the chain, rewriting parts of it or pulling off double spends.
In 2020 alone, ETC got hit hard, with at least three separate attacks that caused major chain reorganizations and let attackers spend the same coins more than once. Outlets like CoinDesk and Wired covered the incidents at the time, and they definitely rattled confidence in the network’s security. In response, project developers implemented MESS (Modified Exponential Subjective Scoring), a mitigation strategy that delays finality for large reorgs. While MESS has made attacks more difficult, some security researchers remain skeptical about its effectiveness compared to economic deterrence models like PoS.
ETH’s economic security model: Staking and validator set considerations
With Ethereum’s move to Proof of Stake, the way the network stays secure changed pretty dramatically. Instead of miners doing the heavy lifting, the system now depends on people staking their ETH - basically locking it up to take part in validating blocks. Validators are rewarded for honest behavior, and going offline or acting maliciously could cost them. Acquiring enough Ether and staking it to attack the system is both risky and costly. Plus, there are thousands of validators spread across the globe, which makes censorship or control by a small group a lot harder.
That said, staking isn’t completely effortless for both ETC and ETH. People who stake have to think about when they can lock and unlock their ETH, and they need to stay online or risk penalties. Still, this approach reflects what Ethereum values: flexibility, strong economic incentives, and a security model that can evolve.
Ethereum Classic takes a different route in the ETH vs ETC comparison, staying loyal to a simpler Proof of Work setup that favors predictability and immutability over constant change. These choices say a lot about what each network stands for.
Ecosystem & Developer Activity
When it comes to building, Ethereum is an open-source leader. Developers launch products and services across its rich L2 space. Classic supports smart contracts, but most projects are forks or copies of ETH-based dApps. The difference between Ethereum and Ethereum Classic in developer energy is hard to miss.
ETH’s L2-centric ecosystem or ETC’s niche communities
Ethereum leads by a wide margin in active developer contributions and deployed applications. A big part of that momentum now lives on Layer 2 networks like Arbitrum, Base, and Optimism, where a lot of the real building is happening. These platforms have become hubs for everything from DeFi and NFTs to DAOs and dev tooling. According to the latest numbers from Electric Capital, Ethereum still brings in more full-time Web3 developers than any other chain, and that energy continues to push the project forward.
In contrast, Ethereum Classic maintains a smaller but dedicated community. While ETC is fully EVM-compatible and capable of running smart contracts, it hasn’t seen the same level of Ethereum protocol growth. Most applications on ETC are forks or derivatives of ETH-based projects, and development efforts tend to focus on core protocol stability and mining support rather than cutting-edge dApps.
For builders, Ethereum offers far more resources, integrations, and user liquidity - making it the dominant platform for launching and scaling blockchain-based products.
Which One Fits Your Goal? (Decision Guide)
Whether you want to earn yield, mine with GPUs, or just send cheap transfers, your choice between Ethereum Classic vs Ethereum depends on your goals. The Ethereum blockchain is better for staking, NFTs, DeFi, and L2s. Classic sticks with the “code is law” ethos and suits those who value simplicity and predictability in a blockchain.
If the goal is yield & network effects → Ethereum (ETH)
Staking this asset or using liquid staking tokens (LSTs) offers passive yield
Tap into the largest dApp and DeFi spaces
Great for NFT minting, DAO participation, and leveraging L2s for fast, low-fee UX
If the goal is GPU mining or immutability ethos → Ethereum Classic (ETC)
This remains one of the few major chains still using Proof of Work
Appeals to miners with existing GPU hardware setups
Aligns with the "code is law" philosophy and a fixed-supply model
Classic sticks with the “code is law” ethos and suits those who value simplicity and predictability in a blockchain.
If the goal is low fees for simple transfers → ETH
L2s Rollups like Optimism and Arbitrum offer fast, cheap transfers
Ideal for remittances, on-chain games, and micro-transactions
Same Ethereum security, lower costs post-Dencun
Please note, staking involves lockup periods and slashing risks. Mining requires hardware investment and power costs. Classic’s history includes multiple reorgs - always consider security trade-offs.
How to Swap on SimpleSwap
Swapping between these two (or any two) assets is easy and secure on SimpleSwap. Here’s how to do it step by step:
Choose the crypto pairSelect ETH in the “You send” section and enter the amount you wish to exchange. Then choose ETC in the “You get” section. Click “Exchange”.
2. Add the recipient’s addressEnter the recipient’s ETH address. The ETH will be sent to this address after the exchange.
3. Send the depositYou’ll see an address to send the indicated amount of ETC to continue your swap.
4. Get cryptocurrenciesAfter receiving your deposit, SimpleSwap will convert it and send the ETH to the wallet address you provided.
SimpleSwap recommends double-checking wallet addresses before submitting, verifying that the receiving wallet supports the correct network when dealing with ETC vs ETH (ETH = Ethereum mainnet; ETC = Ethereum Classic).
Quick security checklist
Validate the recipient address carefully
Use a small test amount if unsure
Confirm the correct chain (ETH ≠ ETC)
That’s it - no sign-ups, just smooth crypto swaps in minutes.
FAQs & Common Misconceptions
Below are a few questions that readers most commonly ask.
Is Ethereum Classic the original Ethereum?
Yes - Ethereum classic preserves the original Ethereum ledger after the DAO hack. Ethereum adopted the forked state to reverse the exploit.
Does Ethereum (ETH) have a fixed supply?
No. This coin has no hard cap, but EIP-1559 introduced a burn mechanism that can reduce total supply over time.
Is Ethereum still expensive to use?
Not on Layer 2s. Post-Dencun, rollups like Optimism and Arbitrum offer drastically lower fees than mainnet.
Can Ethereum Classic run smart contracts?
Yes. Ethereum Classic is EVM-compatible and can run Solidity-based contracts - though the community is smaller.
Can I stake ETC like ETH?
No. ETC uses Proof of Work and doesn’t support staking. ETH uses PoS and offers yield for validators and LST holders.
Is ETC still vulnerable to attacks?
ETC implemented MESS after 2020’s 51% attacks, which helps mitigate reorg risks - but it doesn’t eliminate them.
Summary
By now, readers are likely to be able to tell what's the difference between Ethereum and Ethereum Classic. Ethereum and Ethereum Classic come down to purpose and philosophy. ETH has evolved rapidly with PoS, Layer 2 scaling, and a thriving space ideal for staking, DeFi, and low-fee transactions. ETC remains committed to Proof of Work, a fixed supply, and the principle of immutability - making it a fit for miners and purists.
Your choice should align with your goals, whether that’s earning yield, running a GPU rig, or prioritizing simplicity. When you’re ready to switch between the two, SimpleSwap offers a fast, secure, and user-friendly way to swap ETH and ETC without hassle.